TRIAL International, Human Rights and Justice Centre and Advocacy Forum developed a leaflet on the status of the implementation of decisions on 29 cases (between 2008 and August 2022) rendered by the Human Rights Committee on applications lodged by individuals or groups of individuals against Nepal. The website includes 28 decisions and excludes information on the individual complaint of Charles Gurumukh Sobhraj (decided on 27 July 2010).
Implementation fact sheet
IMPLEMENTATION STATUS
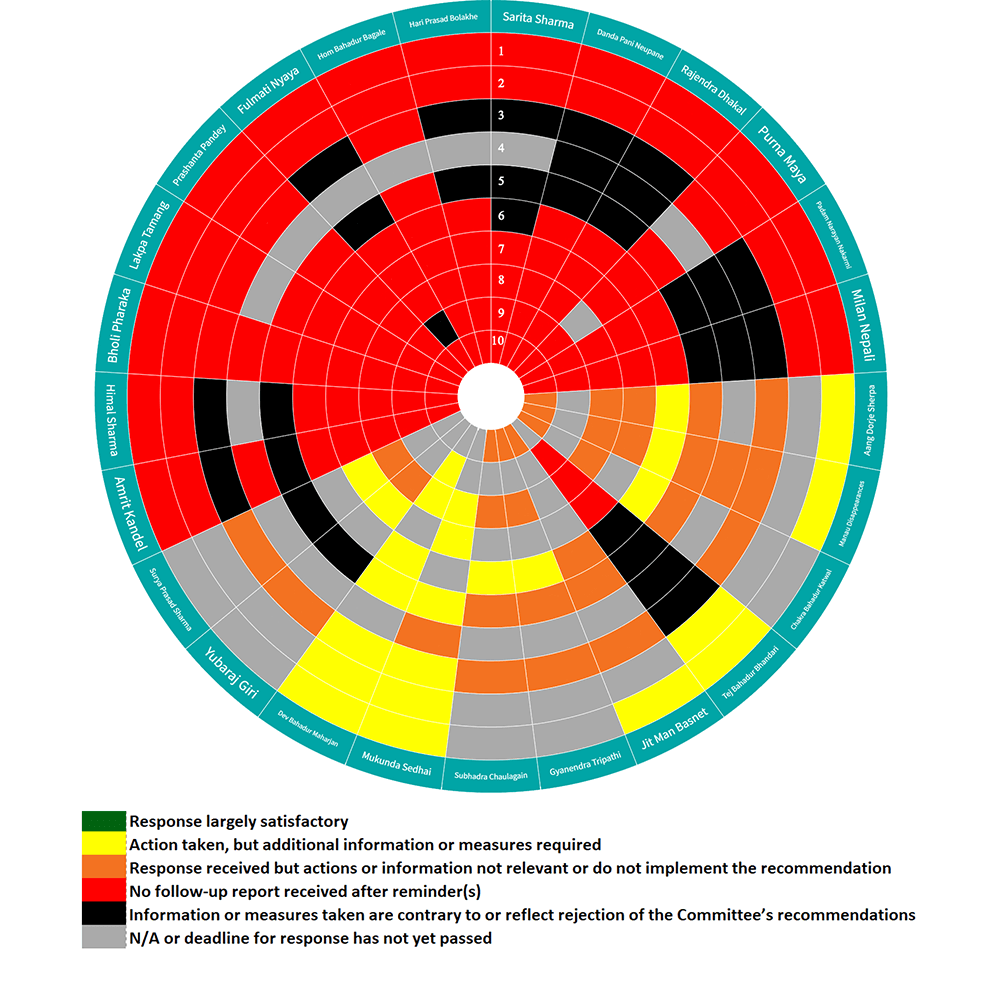
- First circle: Translation of the decision of the HRC into local language
- Second circle: Dissemination of the translated version of the decision
- Third circle: Investigation into the facts of the case
- Fourth circle: Information on the investigation and in case of death, locate the remains and hand over to the family
- Fifth circle: Prosecute and punish the perpetrator of the violation
- Sixth circle: Provide Adequate compensation to the victims
- Seventh circle: Provide rehabilitation to the victims
- Eighth circle: Guarantee non repetition of the similar violation in the future
- Ninth circle: Amend legislations
- Tenth circle: Ensure measures of satisfaction to the victims
Go to the cases database
At its 118th session, on 4 November 2016, the Committee decided to revise its assessment criteria.
Assessment criteria (as revised during the 118th session)
Assessment of replies:
New HRC grading system
| Response largely satisfactory | |
| Action taken, but additional information or measures required | |
| Response received but actions or information not relevant or do not implement the recommendation | |
| No follow-up report received after reminder(s) | |
| Information or measures taken are contrary to or reflect rejection of the Committee’s recommendations |
Explanation of Remedies
Translation and dissemination
Nepal must translate the decision of the Human Rights Committee from English to Nepali and make these decisions widely available to the public.
Investigation of the facts
Nepal must open a formal investigation into the crime(s) committed in an effort to establish the facts of the case and identify the person(s) responsible. Such investigations must be prompt, thorough and impartial.
Information on investigation
Nepal must provide the victim and/or the victim’s family with detailed information on the results of the investigation.
Release or location and return of remains
If the victim is still alive he or she must be released immediately. In the event that the victim is deceased, Nepal must take appropriate steps to locate, exhume and identify his or her remains and return these to the family.
Providing adequate compensation
Nepal must provide victims with monetary payments as a form of reparation to recognise and rectify – as far as possible – the harm suffered. Payments received through the government’s “Interim Relief Program” do not constitute adequate compensation/reparation.
Rehabilitation or Providing psychological rehabilitation/medical treatment
Nepal must make available (or reimburse) necessary services to victims to allow the rehabilitation for the harm suffered as a consequence of the violations to be as full as possible. Such services may include, for example, medical treatment or psychological support, as well as social and legal services.
Prosecution (and punishment) of perpetrators
Following an investigation into the facts, Nepal must initiate criminal proceedings to ensure that the perpetrators are brought to justice.
Providing full reparation
Nepal must provide victims with measures to fully recognise and repair the harm caused by the violation, including providing appropriate compensation, rehabilitation and measures of satisfaction, such as public apologies, public memorials, guarantees of non-repetition and changes in relevant laws and practice.
Prevention of similar violations
Also known as ‘guarantees of non-repetition’, Nepal must take steps to ensure that similar violations will not happen again in the future. This may include general measures, such as changes to domestic legislation and reform of institutions.
Amendment of legislation
Nepal must ensure that its domestic laws conform to the obligations it has under the ICCPR. The Parliament must therefore enact changes to the existing law to prevent future violations and to enable the prosecution of specific crimes – such as torture and enforced disappearance – in its national system.
Protection from reprisals (and intimidation)
Nepal must take measures to ensure that victims and their families are not further victims of harassment or subjected to intimidation and other retaliatory acts in view of their search for justice.
Measures of satisfaction
Nepal must take measures that publicly acknowledge the responsibility of the State and formally recognise the harms suffered by the victims and their families. Examples may include a commemoration to the victims or a public apology.
